The following is a quick tutorial on using the ServiceNow API with python to programmatically create and update configuration items. A personal development instance of ServiceNow Jakarta was used for testing the code below.
About The ServiceNow API
ServiceNow uses a REST Table API that allows users to perform create, read, update and delete operations on existing tables. ServiceNow also provides you with a REST API Explorer that uses information from your instance to provide you with a list of endpoints, methods, and variables that you can use to build and send a REST request. This explorer can be found by navigating to ‘System Web Services’ -> ‘REST API Explorer’.
NOTE: Before accessing the API, be sure your user role is either web_service_admin, rest_api_explorer, or admin. If this is not the case, then you will either need to contact your system administrator or login with an administrator account to change it as follows:
- Type “users” in the filter navigator
- Click on “Organization” -> “Users”
- Click on the user that you want to change
- Scroll to the “Roles” section at the bottom and click “Edit”
- Add the role(s) you want to give the user and click “Save”
The picture below shows the REST API Explorer with the endpoint for the request and a drop-down with all the tables that can be used:
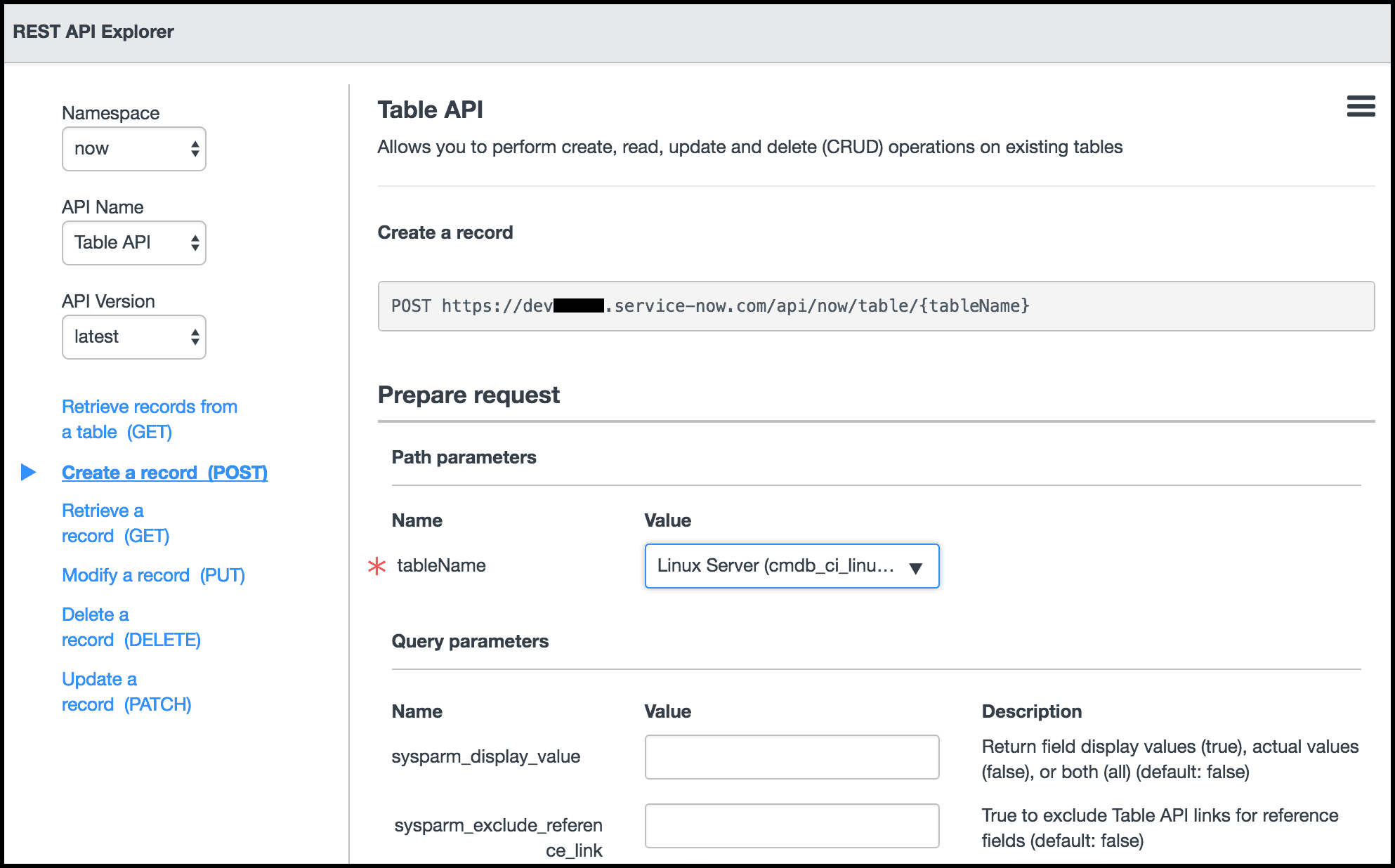
After selecting your table you can scroll down to the “Result Body” section to see the attributes that can be added to the CI. Once these attributes are selected, you can click “Send” to send the POST request and see the response.
Getting Started
The Python “Requests” library makes it easy to connect to your ServiceNow instance and is used in each example below. It can be installed with the following pipenv (or pip) command. The Github page for this library can be found here: https://github.com/requests/requests
pipenv install requests
Adding A New Configuration Item
Below is a basic example of adding a configuration item to the cmdb_ci_linux_server_list table in ServiceNow. A list of tables that you can add CIs to can be found in the REST API Explorer mentioned above, as well as a list of available attributes for CIs in that table.
import requests
# Check the REST API Explorer for the list of tables
table_name = "cmdb_ci_linux_server"
# Determine the ServiceNow url
url = "https://dev12345.service-now.com/api/now/table/{0}".format(table_name)
headers = {'Content-type': 'application/json', 'Accept': 'application/json'}
# A list of attributes for your table can be found in the API Explorer
# These values will differ depending on the table
payload = {
'cpu_count': '1',
'dns_domain': 'domain.com',
'install_status': 'Installed',
'ip_address': '1.1.1.1',
'manufacturer': 'Virtual',
'model_number': 'Virtual',
'name': 'some-server',
'ram': '2048',
'serial_number': 'Virtual',
'short_description': 'Adding this CI to the cmdb_ci_linux_server table'
}
# Save the result of the request in a variable
result = requests.post(url,
json=payload,
headers=headers,
auth=("sn_username", "sn_password"))
# The result will have the sys_id of the new CI
print result.content
Editing A Configuration Item
Each Configuration Item in ServiceNow has its own unique “sys_id”, which can be found in the result of the POST request. Save this sys_id for updating and deleting the CI in the future.
The following example shows how to use that sys_id to change some of the fields of the CI:
import requests
# Check the REST API Explorer for the list of tables
table_name = "cmdb_ci_linux_server"
# The unique ServiceNow sys_id
sys_id = "b9b264230f310300787988cce1050e41"
# Determine the ServiceNow url
url = "https://dev12345.service-now.com/api/now/table/{0}/{1}".format(table_name, sys_id)
headers = {'Content-type': 'application/json', 'Accept': 'application/json'}
# A list of attributes for your table can be found in the API Explorer
# These values will differ depending on the table
payload = {
'install_status': 'Retired',
'short_description': 'Change the install_status of this CI'
}
# Save the result of the request in a variable
result = requests.patch(url,
json=payload,
headers=headers,
auth=("sn_username", "sn_password"))